
Transactions include sales, purchases, and wages paid during the accounting period. Account balances include all the asset, liabilities and equity interests included in the statement of financial position at the period end. The cut-off assertion is used to determine whether the audit management assertions transactions recorded have been recorded in the appropriate accounting period.
What are the 5 (or Audit Assertions?
Audit assertions, also https://www.bookstime.com/ known as financial statement assertions or management assertions, serve as management’s claims that the financial statements presented are accurate. The concept is primarily used in regard to the audit of a company’s financial statements, where the auditors rely upon a variety of assertions regarding the business. The auditors test the validity of these assertions by conducting a number of audit tests. For auditors, it is crucial to ensure amounts recorded in the financial statements are accurate. This way, auditors can ascertain the financial statements are free from material misstatements. Auditors use numerous audit assertions when examining a company’s financial statements.
Strategic Supplier Management in the Financial Sector
The completeness assertion means that all assets, liabilities, and equity accounts that should have been recorded have been recorded. Completeness also means that all the related disclosures that should be included in the financial statements are included. For example, when presenting accounts payable on the balance sheet, the client asserts that no accrued liabilities were omitted from accounts payable whether due to fraud or error.
Rights and Obligations
Auditors for these companies perform procedures to test the validity of management’s assertions and to provide an independent opinion. Tests of controls assess the effectiveness of an entity’s internal controls to prevent, detect, and correct material misstatements. Auditors evaluate the design and implementation of controls and perform tests to determine if they are operating effectively. For example, auditors may test the segregation of duties by observing and reviewing the authorization and approval processes. Furthermore, the historical accuracy of management’s assertions plays a role in their current validity. Auditors consider the entity’s track record, looking for patterns of inaccuracies or misstatements in prior periods.

- When it comes to account balances at year-end, the presentation assertion means the assets, liabilities, and equity accounts are sufficiently aggregated or disaggregated and clearly described.
- At the end of this article, you can also see the summary of all assertions and their usages.
- Auditors must assess whether the claims made by management are supported by adequate and appropriate evidence.
- Likewise, we usually use these assertions to assess external financial reporting risks.
- SOX also created the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB)—an organization intended to assess the work performed by public accounting firms to independently assess and opine on management’s assertions.
Obtaining relevant and reliable audit evidence can be challenging, particularly when dealing with complex transactions or entities that lack adequate documentation. Candidates should ensure that they know the assertions and can explain what they mean. Candidates should not simply memorise these tests but also ensure they understand the reasons why the test provides assurance about the particular assertion. In some instances, the direction of the test will be a key point to consider. Relevant tests – the test for transactions of checking purchase invoice postings to the appropriate accounts in the general ledger will be relevant again.
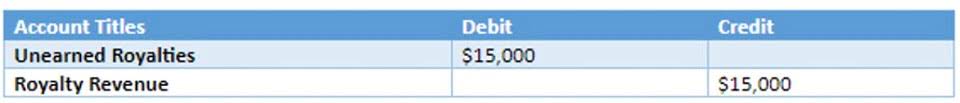
- They use those assertions to guide their work and ensure they meet their objectives.
- To verify that the amount recorded as paid is the same as received from the customer.
- Opposite to right and obligation, we test the audit assertion of cut-off for income statement transactions only.
- As auditors rely on assertions, it is crucial to recognize their significance and the procedures used to test them.
- Auditors review these assertions by examining the financial statements and accompanying notes, ensuring that the disclosures are complete, clearly presented, and free from material misstatements.
The process involves a series of procedures, including inquiry, observation, inspection, and external confirmation, to substantiate the assertions made. The audit assertions can provide us the clues on the potential misstatements that might occur on financial statements. Likewise, we usually use these assertions to assess external financial reporting risks. Audit assertions, financial statement assertions, or management’s assertions, are the claims made by the management of the company on financial statements. The moment the financial statements are produced, the assertions or the claims of management also exist, e.g., all items in the income statement are assured to be complete and accurate, etc. Audit assertions are classified as one of the primitive aspects of auditing.

AccountingTools

Exhibit 7-2 summarizes the relationship between management assertions and general audit objectives for a financial statement audit. Company executives are required to make assertions or claims to the public regarding certain aspects of a https://www.facebook.com/BooksTimeInc/ business. Independent auditors use these representations as the foundation from which they design and perform procedures to test management’s assertions and form an opinion to which they attest to the public. A lot of work is required for an organization to support the assertions that a management team makes. Often controls related to financial reporting extend beyond the immediate company to service organizations supporting its operations.